Notice
Recent Posts
Recent Comments
Link
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
Tags
- sql
- BFS
- 코딩테스트준비
- 공개키 암호화
- 코딩테스트
- Java
- 가상컴퓨팅
- 99클럽 #코딩테스트준비 #개발자취업 #항해99 #til
- 크루스칼
- 코테
- 위상정렬
- 개발자취업
- spring
- javascript
- Algorithm
- 정렬
- JPA
- DB
- js
- 알고리즘
- generic class
- til
- dbms
- 자료구조
- 99클럽
- Sort
- jsp
- 항해99
- python
- 자바의정석
Archives
- Today
- Total
PLOD
[Java]상속(Inheritance) 본문
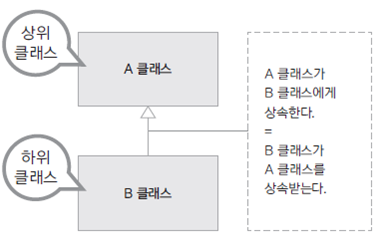
상속(inheritance)
상속이란 기존의 클래스를 재사용하여 새로운 클래스를 작성하는 것이다, 상속을 통해서 클래스를 작성하면 보다 적은 양의 코드로 새로운 클래스를 작성할 수 있고 코드를 공통적으로 관리 할 수 있기 때문에 코드의 추가 및 변경이 매우 용이하다.
위 그림에서, 상위클래스(A)를래스를 parent class, base class, super class 라고 하고 하위에 있는 클래스(B)를 child class, derived class, subclass 라고 한다.
상속에서 자식 클래스와 부모 클래스는 is -a 관계가 성립한다. 반대로 부모 클래스와 자식클래스는
has-a 관계가 성립하게 된다.
자식클래스는 부모클래스에서 확장한다는 의미로 extends 키워드를 사용해 상속 관계를 선언한다.
자바는 클래스 끼리 단일 상속만 허용하고 다중 상속을 하고 싶다면 인터페이스를 사용하면 된다.
ex.
class Parent { ... }
class Child extends Parent{ ... }
Q ) 회사에서 고객 정보를 활용한 맞춤 서비스를 하기 위해 일반고객(Customer)과 이보다 충성도가 높은 우수고객(VIPCustomer)에 따른 서비스를 제공하고자 함
물품을 구매 할때 적용되는 할인율과 적립되는 보너스 포인트의 비율이 다름 여러 멤버십에 대한 각각 다양한 서비스를 제공할 수 있음 멤버십에 대한 구현을 클래스 상속을 활용하여 구현해보기
1) Customer 클래스
//부모클래스 생성 , 변수들은 protected로 설정해준다
public class Customer {
protected int customerID;
protected String customerName;
protected String customerGrade;
protected int bonusPoint;
protected double bonusRatio;
public Customer(int customerID, String customerName) {
this.customerID = customerID;
this.customerName = customerName;
customerGrade = "SILVER";
bonusRatio = 0.01;
}
public int calcBonusPoint(int price) {
bonusPoint += price * bonusRatio;
return bonusPoint;
}
public String showCustomerInfo() {
return customerName + "님의 등급은" + customerGrade +
"이며 , 보너스 포인트는 " + bonusPoint + "입니다.";
}
}매출에 더 많은 기여를 하는 단골 고객
제품을 살때 10%를 할인해 줌
보너스 포인트는 제품 가격의 5%를 적립해 줌
담당 전문 상담원이 배정됨
2) VIP customer 클래스
//자식클래스 생성, VIP 클래스는 더이상의 상속이 없기 때문에 private로 변수 설정
public class VIPCustomer extends Customer{
private int agentID;
private double salesRatio;
// super()를 통해 customerID 와 customerName 상속
// super()를 사용안하고 매개변수 사용시, 오류 발생
public VIPCustomer(int customerID, String customerName) {
super(customerID, customerName);
customerGrade = "VIP";
bonusRatio = 0.05;
salesRatio = 0.01;
}
public int getAgentID() {
return agentID;
}
}3) 실행
public class customerTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Customer customerLee = new Customer(10010, "이순신");
customerLee.bonusPoint = 1000;
customerLee.calcBonusPoint(2000);
System.out.println(customerLee.showCustomerInfo());
Customer customerKim = new VIPCustomer(10020, "김유신");
customerKim.bonusPoint = 10000;
customerKim.calcBonusPoint(2000);
System.out.println(customerKim.showCustomerInfo());
}
}하위 클래스를 생성하면 상위 클래스가 먼저 생성 된다. 위의 코드에서 new VIPCustomer()를
호출하면 Customer()가 먼저 호출 된다. 클래스가 상속 받은 경우 하위 클래스의 생성자에서는
반드시 상위 클래스의 생성자를 호출한다.
*super()
- 하위 클래스에서 가지는 상위 클래스에 대한 참조 값
- super()는 상위 클래스의 기본 생성자를 호출 함
- 하위 클래스에서 명시적으로 상위 클래스의 생성자를 호출하지 않으면 super()가 호출 됨
( 이때 반드시 상위 클래스의 기본 생성자가 존재 해야 함) - 상위 클래스의 기본 생성자가 없는 경우 ( 다른 생성자가 있는 경우 ) 하위 클래스에서는 생성자에서는 super를 이용하여 명시적으로 상위 클래스의 생성자를 호출 함
- super는 생성된 상위 클래스 인스턴스의 참조 값을 가지므로 super를 이용하여 상위 클래스의 메서드나 멤버 변수에 접근할 수 있음
'개발 공부 > Java' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Java] 클래스- 생성자(Constructor) (0) | 2023.01.12 |
|---|---|
| [Java] 접근 제어자(access modifier) (0) | 2022.12.04 |
| [Java] 자바 용어 정리 및 원리 (0) | 2022.11.11 |
| [Java] 추상 클래스(Abstract class) , 메서드(Method) (0) | 2022.11.09 |
| [Java] 참조 자료형 (0) | 2022.11.08 |
Comments




